Android Motion: Touch Feedback
Touch Feedback helps add nice animation to signify view interactions like clicks and long clicks.
It can be implemented in the following ways
-
For simple bounded ripple effects on your view, set its background to
?android:attr/selectableItemBackground -
For unbounded ripple effect, set the view’s background to
?android:attr/selectableItemBackgroundBorderlessThe ripple effect extends beyond the originating view and ends at the bounds of its immediate non null parent. This requires API >= 21.
-
Using a
RippleDrawable. (Requires API >= 21)
ARippleDrawablecan be used in two ways, xml and Java. Before we proceed, it’s important to understand what a Mask is. A mask is a layer that defines the bounds of the ripple effect
-
For an unbounded ripple effect (with no mask)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <ripple android:color="@color/unbounded_ripple" xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" /> -
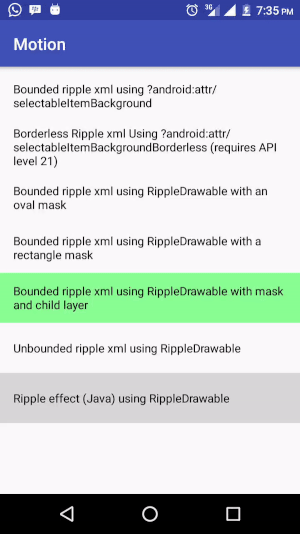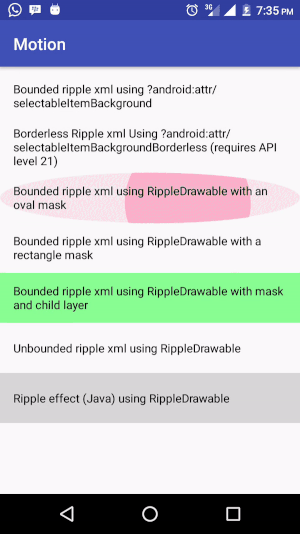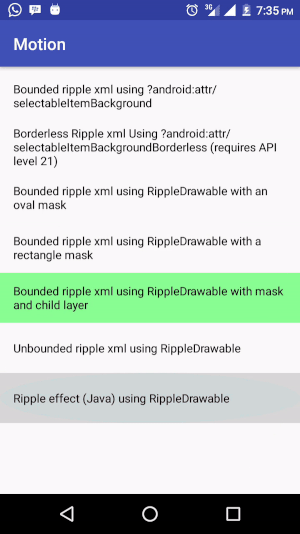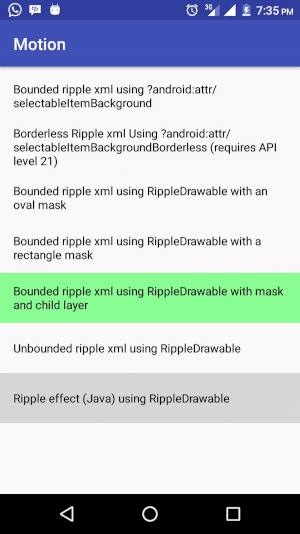
For a bounded ripple with an oval mask
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <ripple android:color="@color/colorAccent" xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"> <item android:id="@android:id/mask"> <shape android:shape="oval"> <solid android:color="@color/colorAccent"/> </shape> </item> </ripple> -
For a bounded ripple with a rectangular mask
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <ripple android:color="@color/blue" xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"> <item android:id="@android:id/mask"> <shape android:shape="rectangle"> <solid android:color="@color/blue"/> </shape> </item> </ripple> -
For a bounded ripple with a rectangular mask and a child layer (base background)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <ripple android:color="@color/colorAccent" xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"> <item android:id="@android:id/mask"> <shape android:shape="oval"> <solid android:color="@color/colorAccent"/> </shape> </item> <!--child layer--> <item android:drawable="@color/green" /> </ripple> -
For bounded ripple effects in Java
TextView textView_ripple_drawable = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.textView_ripple_drawable_java); int[][] states = new int[][] { new int[] { android.R.attr.state_enabled}, // enabled new int[] {-android.R.attr.state_enabled}, // disabled new int[] {-android.R.attr.state_checked}, // unchecked new int[] { android.R.attr.state_pressed} // pressed }; int[] colors = new int[] { Color.CYAN, Color.RED, Color.GREEN, Color.YELLOW }; ColorStateList colorStateList = new ColorStateList(states, colors); if (android.os.Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP) { ShapeDrawable shapeDrawable = new ShapeDrawable(new OvalShape()); //ColorDrawable contentColor = null; ColorDrawable contentColor = new ColorDrawable(ContextCompat.getColor(this,R.color.grey)); RippleDrawable rippleDrawable = new RippleDrawable(colorStateList, contentColor, shapeDrawable); textView_ripple_drawable.setBackground(rippleDrawable); } else { Toast.makeText(this, "Requires API >= 21", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); }The
contentColorvariable when set to null, gives the view the default background. To set the bounds of the ripple to that of the view, simply set theshapeDrawablevariable to null.
Below is a clip showing the ripple effect generated from different implementations
References
1. RippleDrawable
2. Exploring Meaningful Motion on Android
3. Defining Custom Animations
